While actively engaged in multiple opportunity zone investor marketing projects raising $120mn, I had the privilege of delving deeper into the intricacies of opportunity zones. This journey has allowed me to grasp the concept of opportunity zones, recognize their associated advantages, and comprehend why investors should incorporate them into their real estate investment strategies. Join me in exploring the world of opportunity zones through the insights shared in this blog post
What are Opportunity Zones?
An Opportunity Zone is a designated economically distressed community or area in the United States that is eligible for certain tax incentives to encourage investment and economic development. These zones were established as a part of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 to stimulate private investment in low-income and disadvantaged areas.
Here are some key aspects of Opportunity Zones:
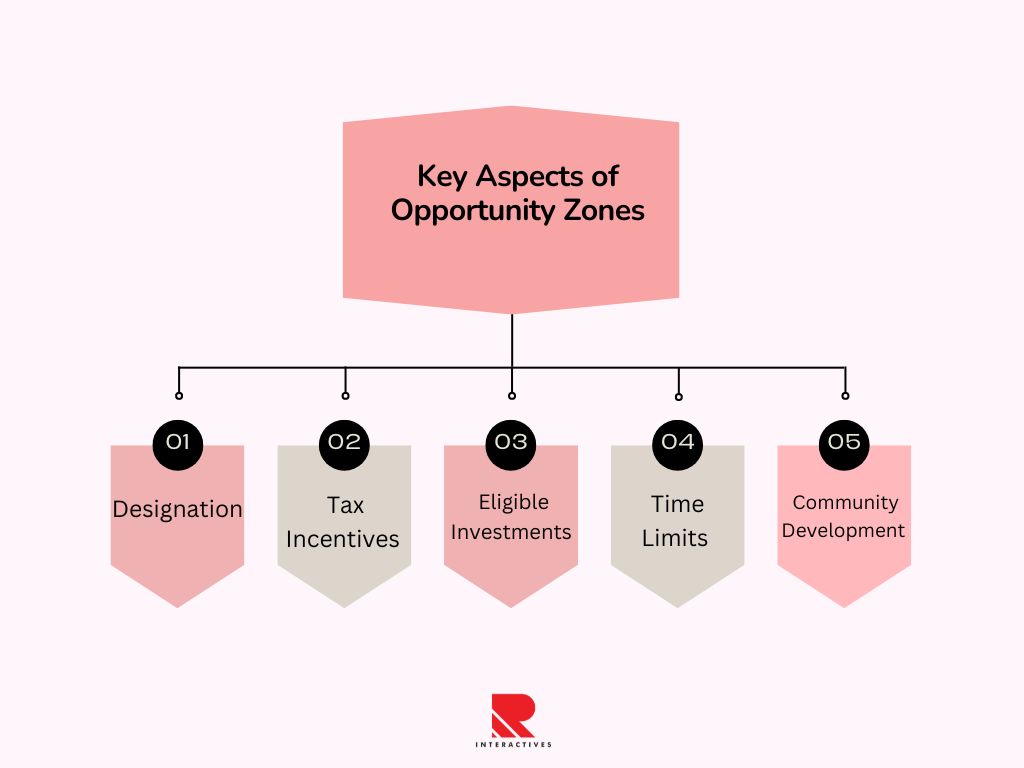
1. Designation:
Opportunity Zones are selected by each state’s governor based on criteria provided by the U.S. Treasury Department. These zones are typically located in areas with lower income levels and in need of revitalization.
2. Tax Incentives:
Investors who put their capital gains from other investments into Qualified Opportunity Funds (QOFs), which are investment vehicles that focus on projects within Opportunity Zones, can benefit from several tax incentives. These incentives include temporary deferral of capital gains taxes, a reduction in the taxable amount of those gains if the investment is held for a certain period, and the potential for tax-free gains on investments held in the QOF for an extended period.
3. Eligible Investments:
Qualified Opportunity Funds can invest in various types of projects, including real estate development, businesses, and infrastructure, within the Opportunity Zone. The goal is to promote economic development, job creation, and community improvement in these areas.
4. Time Limits:
To maximize the tax benefits, investors must adhere to specific timeframes for their investments in Qualified Opportunity Funds, including holding periods.
5. Community Development:
Opportunity Zones aims to attract private investment to communities that may have been overlooked in the past, helping to fund projects that can improve housing, infrastructure, and economic opportunities for residents.
Opportunity Zones have garnered significant attention from investors, developers, and policymakers as a way to promote both economic growth and social impact in disadvantaged communities.
What are the benefits of investing in Opportunity Zones?
Investing in Opportunity Zones offers several potential benefits for investors, which primarily revolve around tax incentives and the potential for financial returns. Here are some of the key advantages of investing in Opportunity Zones:
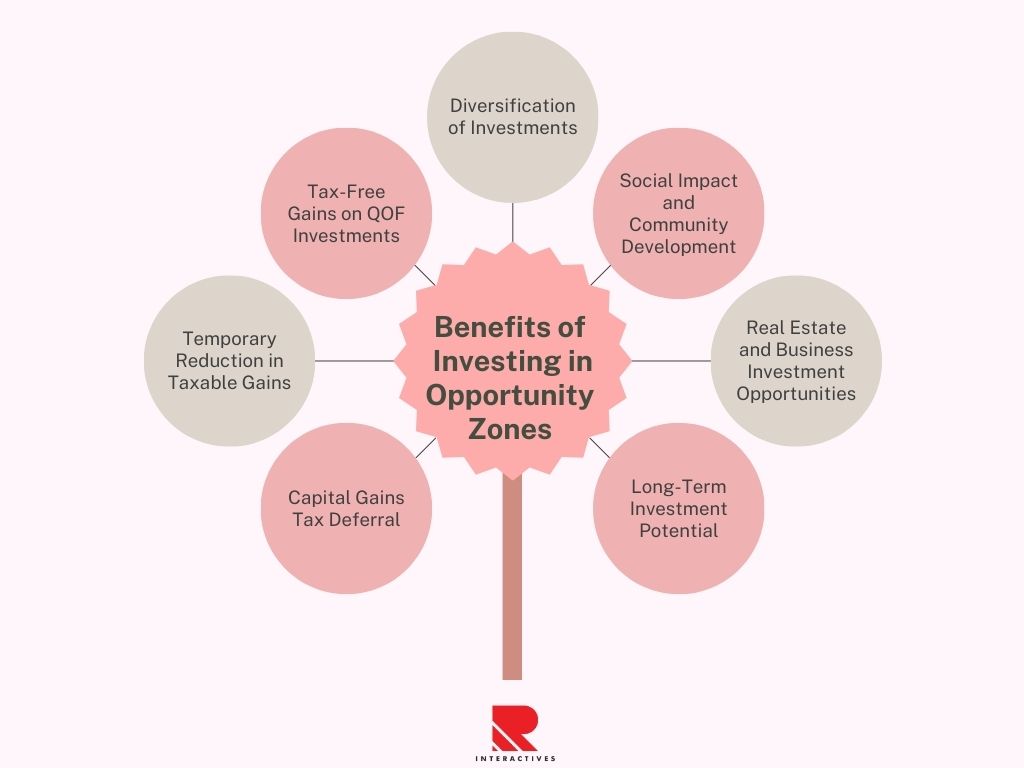
1. Capital Gains Tax Deferral:
One of the primary benefits is the ability to defer capital gains taxes. Investors can defer the taxes on their eligible capital gains by reinvesting those gains into a Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF) within 180 days of the sale or exchange that generated the capital gains. This deferral can provide investors with immediate tax savings.
2. Temporary Reduction in Taxable Gains:
In addition to the deferral, investors may be eligible for a temporary reduction in the taxable amount of their reinvested gains. If they hold their investment in the QOF for at least five years, they can receive a 10% reduction in the amount of the deferred gain that is taxable. If they hold it for at least seven years, they can receive an additional 5% reduction (for a total of a 15% reduction).
3. Tax-Free Gains on QOF Investments:
Perhaps the most significant potential benefit is the opportunity to realize tax-free gains on the investment in the QOF itself if it is held for at least ten years. This means that any appreciation in the value of the investment within the QOF is exempt from capital gains tax when it’s sold.
4. Diversification of Investments:
Opportunity Zones offer a way for investors with significant capital gains in other investments (such as stocks or real estate) to diversify their portfolios while still deferring and potentially reducing their tax liability.
5. Social Impact and Community Development:
Beyond the tax benefits, investing in Opportunity Zones allows investors to contribute to the economic revitalization and development of disadvantaged communities. This can align with the goals of impact investing and corporate social responsibility.
6. Real Estate and Business Investment Opportunities:
Qualified Opportunity Funds can invest in a variety of projects, including real estate developments, startup businesses, and infrastructure projects. This provides investors with a range of investment options to choose from based on their risk tolerance and investment objectives.
7. Long-Term Investment Potential:
The tax benefits associated with Opportunity Zones are generally tied to long-term investment horizons (e.g., holding the investment for at least ten years). This encourages patient capital and long-term commitment to the community.
It’s important to note that while there are potential tax benefits associated with Opportunity Zone investments, these investments also carry risks, and the tax rules can be complex. Investors should carefully consider their individual financial situation, consult with tax professionals, and conduct thorough due diligence on the specific investment opportunities within Opportunity Zones to make informed decisions. Additionally, the program’s regulations and rules may change over time, so staying informed about the latest developments is crucial.
How Does Opportunity Zones Work?
Project Type: Affordable Housing Development
Location: An Opportunity Zone in a mid-sized city.
Description:
In this example, a real estate developer identifies a parcel of land located within an Opportunity Zone. The developer plans to build an affordable housing complex on the vacant land to address the shortage of affordable housing in the area. The project includes the construction of apartment buildings with a mix of one-bedroom and two-bedroom units.
Funding Structure:
To finance the project, the developer establishes a Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF), which will serve as the investment vehicle for attracting capital from investors seeking to take advantage of the tax benefits offered by the Opportunity Zone program.
Investor Participation:
High-net-worth individuals, accredited investors, and institutional investors interested in the tax incentives associated with Opportunity Zones decide to invest in the QOF. They do so by rolling over capital gains from previous investments (e.g., the sale of stocks or real estate) into the QOF within the required timeframe.
Use of Funds:
The capital raised through the QOF is used to fund various aspects of the affordable housing development project, including land acquisition, construction costs, permitting fees, and other development expenses.
Tax Benefits for Investors:
- Capital Gains Tax Deferral: Investors defer the capital gains taxes on the rolled-over funds until December 31, 2026, or until they sell their investment in the QOF, whichever comes first.
- Reduction in Taxable Gains: If investors hold their investment in the QOF for at least five years, they receive a 10% reduction in the taxable portion of their deferred gains. If they hold it for at least seven years, they receive an additional 5% reduction, for a total reduction of 15%.
- Tax-Free Gains on QOF Investment: If investors hold their investment in the QOF for at least ten years, any capital gains generated from the QOF investment are exempt from federal capital gains taxes when they sell their interest in the QOF.
Community Impact:
The affordable housing development project addresses a pressing community need by providing quality housing at lower rental rates. It creates jobs during the construction phase and potentially contributes to the revitalization of the Opportunity Zone by increasing the local housing supply and attracting residents and businesses.
Exit Strategy:
After the ten-year holding period, investors may choose to sell their interest in the QOF, realizing tax-free capital gains on their QOF investment if they meet the program’s requirements.
This example illustrates how Opportunity Zone investments can fund projects that align with community development goals while providing tax benefits to investors who commit to long-term investments in economically distressed areas. It’s important to note that Opportunity Zone projects can vary widely in type and scope, including real estate development, small business investments, and infrastructure projects, among others. Each project aims to drive economic growth and positive social impact within Opportunity Zones.
If you are an opportunity zone fund, and looking to raise funds, reach out to us at R Interactives