If you are starting a new online business or a startup or you are an existing business & have introduced a new product, you would want your customers to buy or upgrade at the earliest. In short, you want them to quickly adopt your product or service. That’s all that is there for customer adoption, but you will have to help your customers to hasten the process and achieve desired outcomes. In this post, we will discuss various aspects related to customer adoption in detail. When a startup launches a new product, they are looking for customer adoption, so the initial set of customers are going to decide whether the product would be accepted or not, so let’s understand customer adoption in detail
What Is Customer Adoption?
In simple terms, customer adoption refers to the process employed by a business that introduces a new product or service for the consumption of its target audience. It enables the company’s existing and potential customers to adopt and acquire the product or service. It comprises various aspects right from the moment the company’s audience becomes aware of the newly introduced product or service to the time they integrate the same into their lives.
This means that your customers need to be guided through a period during which they consider your product and until they reach the stage of actually adopting it. This also means that you need to have a clear understanding of the customer adoption lifecycle in order to ensure that the process is smoother and you achieve optimum user adoption ratios. Now, before any discussion on how you can improve the customer adoption lifecycle, it is important to understand the customer adoption curve.
Customer Adoption Curve
The customer adoption curve can be considered a tool that businesses can use to classify their audience into different categories. This is done on the basis of their interest in new technology and ideas. Using this tool, your audience can be categorized into five types:
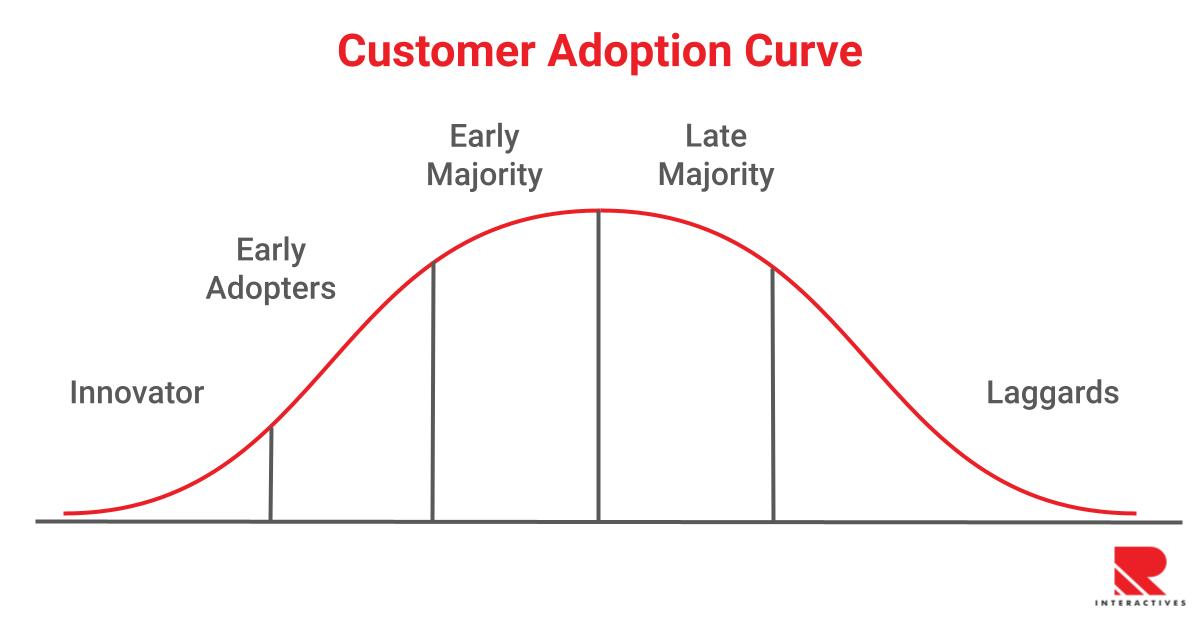
1. Innovators
A few of your target audience will be ready to take risks. They are referred to as innovators. They are people who think outside the box and willingly buy your newest product or service and makeup 2.5 percent of the population. Typically, they don’t wait for the new product or service to be proven and often come up with their own ideas.
2. Early Adopters
Early adopters are comfortable taking risks and are often trendsetters. They use a product or service to form their own opinion and then promote its use. They are often the first people to know about a new product or service. The aspect that separates early adopters and innovators is the former’s concerns regarding their reputation. Innovators don’t mind failing publicly. The traits of an early adopter include persuasiveness, a willingness to work through bugs and initial setbacks, and concern about their reputation. Approximately 13.5 percent of your audience belongs to this category.
3. Early Majority
As much as 34 percent of your target audience belongs to this category. This category of people will be logical, practical, and data-driven. They are interested in new products and services but need proof that they are effective. These people scour product reviews before making a purchase. Furthermore, they quietly conduct some research before committing. You need to formulate a pragmatic approach to convert them into your customers.
4. Late Majority
Thirty-four percent of your target audience can be included in this category. They are logical and cautious people, and they don’t like to take any kind of risk. Like the people belonging to the early majority category, these people will look for a data-driven reason to buy a product or service. A lot of effort may be required to convince people who fall into this adopter category. You will have to provide solid proof that the product or service is worth trying out.
5. Laggards
Laggards constitute 16 percent of your audience group. They are skeptical, resistant to change, and exercise great caution when it comes to buying new products or services. Before getting on board, laggards need to know how they will benefit. This category of people prefers to maintain the status quo because there will be no uncertainties. They are stubborn users and get frustrated easily.
What are the Different Customer Adoption Metrics to Look At?
In order to improve customer adoption, it is important to measure certain metrics. Adoption monitoring is beneficial in obtaining product feedback as well. In addition to looking at just the adoption of your whole product or service, you get insight into the specific features that your users like. This will be of great help to your product and sales teams. Furthermore, measuring adoption also enables you to ensure that you are achieving business goals you are looking at
The three key metrics related to customer adoption are:
#1: Adoption Rate
The adoption rate is calculated as follows:
 This is the most basic metric as far as adoption is concerned. However, it is very useful baseline data that comes in handy. For example, if 250 users out of the 1,000 you currently have buy your new product, your adoption rate is 25 percent. This metric can be used to measure the adoption of not only your whole product but also a specific feature. Furthermore, the adoption rate is generally calculated for a specific time period.
This is the most basic metric as far as adoption is concerned. However, it is very useful baseline data that comes in handy. For example, if 250 users out of the 1,000 you currently have buy your new product, your adoption rate is 25 percent. This metric can be used to measure the adoption of not only your whole product but also a specific feature. Furthermore, the adoption rate is generally calculated for a specific time period.
#2: Customer LifeTime Value (CLTV)
Customer lifetime value (CLTV or CLV) is another key statistic to track to better understand customer adoption. CLV measurement helps you understand the value of a customer to your business, not on the basis of each purchase but over the period of their relationship with your organization. This is an important metric because it highlights the fact that it costs less to retain existing customers rather than acquire new ones. This is to say that increasing existing customers’ value is one of the best ways to drive growth. Therefore, knowing the CLV allows you to implement strategies to not only retain existing customers but also acquire new ones.
Customer Lifetime Value (cLTV) Formula

#3: Customer Churn Rate
“Customer churn rate” refers to the percentage of customers you lose during a specified period of time. For mobile apps or SaaS, it means the number of customers cancelling their subscription. For eCommerce businesses, it means the number of customers failing to make repeat purchases within the specified time frame (30, 90, or 120 days). Typically, the churn rate is calculated on the basis of paying customers. Therefore, customers who are trying out your product or service without paying should be excluded from your calculations. Furthermore, the churn rate is concerned about customers lost rather than the change in revenue.
The customer churn rate is calculated as follows:

Customer Adoption Journey
It is a fact that measurement of customer adoption metrics is essential to improve the adoption rate. However, it is important for you to know the stages through which a lead goes before becoming a loyal customer. This would enable you to customize the information you provide depending on which stage the lead is in. Each customer passes through five stages in their purchase journey. They are:
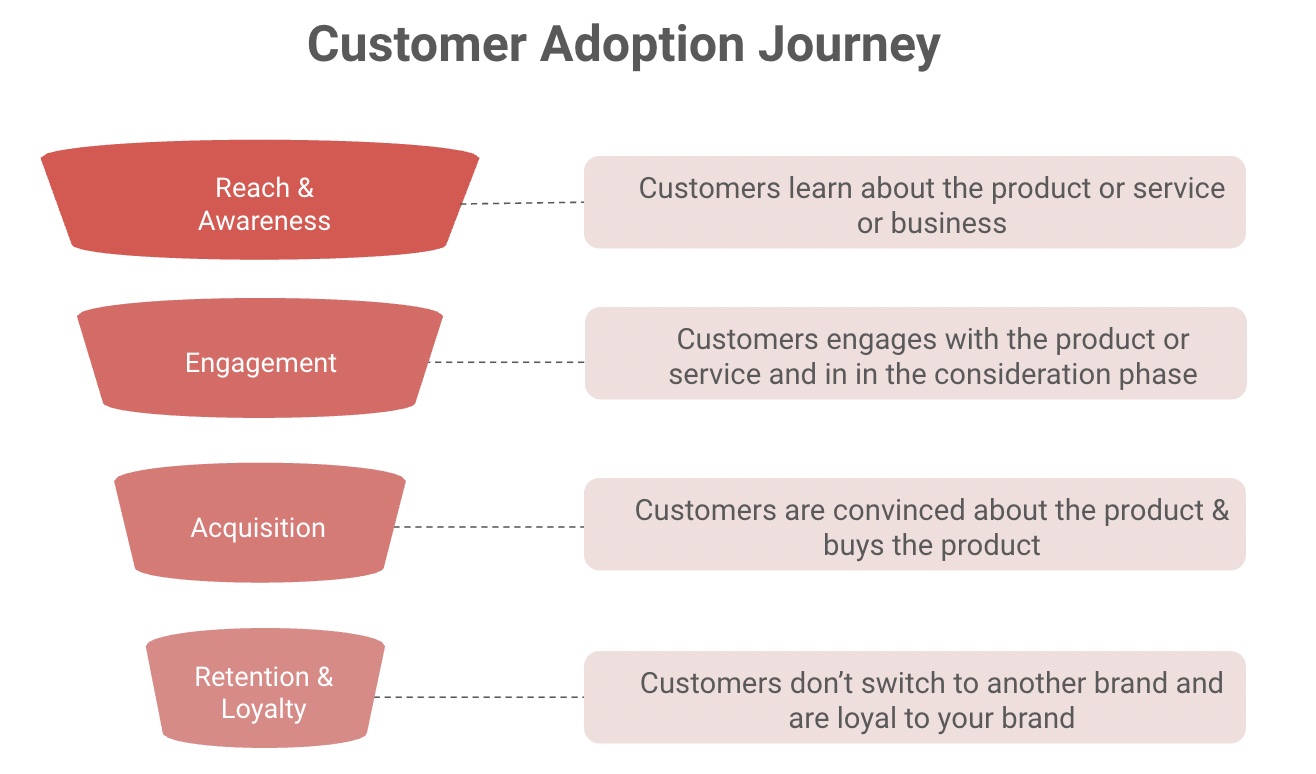
Reach and Awareness
The starting point of a customer’s adoption journey is reach and awareness. The consumer comes to know of the new product or service but may not have enough information about it. Once a consumer becomes aware of a new product or service, they may become interested in it and may seek more information. You can inform your audience about the new product or service through advertisements, publicity, or other marketing efforts.
Engagement
Some of your customers will seek information, and once they have understood how the product or service can be beneficial to them, they will move into the evaluation stage. They may also consider acquiring a new product or service. However, you need to keep them engaged by providing more value-added information such as features, uses, benefits, disadvantages, location, and price.
Product or service acquisition
Establishing contact and converting prospects into customers is what makes up the acquisition process. Interaction and engagement are the key elements that define potential customers. In today’s digital age, you can go a step ahead and employ consumer-targeted campaigns that are backed by data which influence their decisions.
Customer retention
Retention is an umbrella term and consists of smaller phases such as onboarding, adoption, support, engagement, and expansion. The goal is to maintain customer satisfaction by proactively responding to challenges. Engaging with customers on a regular basis will enable you to have a clear picture of the needs of your customers. Simultaneously, you work towards finding unique, new solutions.
Building loyalty
Keeping track of the reviews posted by your customers and your review ratings is important to ensure that your prospects go through a healthy customer journey. At the same time, you need to track loyalty by cutting down on the churn rate and increasing renewals. Referral programs, loyalty programs and effective tracking can help you get a clearer picture of customer loyalty.
How to Increase Customer Adoption?
Now that you have some ideas about customer adoption, different categories of customers, the metrics involved, and the journey a customer goes through before buying your product or services, it is time to learn how to increase your customer adoption rate. The steps involved are:
#1. Start with a Minimal Viable Product
A minimum viable product is a version of the new product you are planning to introduce to the market. This helps you to derive a great deal of validated information about your audience. This is because coming up with the right product for your audience is a challenging task. You need to do sufficient research and create different prototypes prior to launching the final product. Another aspect that you need to consider when introducing the final product is the completeness of the product. This is when the concept of creating an MVP will be of great help to you. Many businesses, such as Dropbox, Zappos, and Uber, started off with MVPs before becoming hugely successful.
The advantages of starting with an MVP are:
- Lower implementation costs
- Reduced capital losses and product failures
- Shortest time to market
- Allows testing of product demand before launching the final full version
- Helps gain in-depth and valuable insights into what the market wants
- Helps analyze the interests and behaviours of consumers
#2. Test Your Product with a Set of Existing Customers
It is a good idea to go through a beta test when planning to roll out a new product or feature. This will help you clearly understand how the product or feature works. You can obtain feedback from users and rectify the issues before finally launching the product. When conducting beta testing, you should make the product or feature available only to a few of your existing customers.
#3. Learn from Customer Feedback
After beta testing, learn from customer feedback. Listen carefully to what your customers are saying about the product. It is a good idea to ask them to provide feedback by responding to a survey. This will help you learn what works for your customers and what does not. This way, you can increase your adoption rate by providing what your customers are really looking for.
#4. Follow the Build-Measure-Learn Loop
“Build-Measure-Learn” is by far the most important lean startup principle. It is a highly effective way to build a product successfully. “Build-Measure-Learn” can be considered as a framework that helps you establish and continuously improve the effectiveness of new products or services in a cost-effective manner.
In practice, it involves a cycle of building and testing hypotheses. You start small; you give the product to potential customers and ask them to try it out, measure their reactions, and learn from the results. The goal is to improve your product continuously so that you are in a position to eventually deliver exactly what your customers are looking for.
The simple-sounding framework can actually be a game-changing technique for your business.
#5. Offer a Free Trial
This is yet another strategy that you can employ for increasing your new product adoption rate. You can make things simple and easy by offering your customers a free trial of your new product. Giving a few of your potential customers a free trial for 30 days is one of the most powerful ways to get them to use your product quickly and continue using it after the trial period. A trial is one of the critical elements when it comes to accelerating adoption. This is because trials often lead to sales, repeat purchases, and referrals.
#6. Improve User Experience
Ultimately, customers will adopt your product only if they have an excellent experience using it. Otherwise, they will discard your product. This means that you will have to focus on the quality of the product you are developing for your customers. The product or service that you want to offer to your customers should add value, be intuitive, and be simple to use. If you focus on improving customer experience by continuously enhancing your product, there is no doubt that they will quickly adopt your new product as and when you release it to the market.
Conclusion:
It is not wise to offer a new product to your customers assuming that they will definitely buy it. The approach – build a product and customers will buy it anyway – doesn’t work any longer. It is important to have a clear idea of the user adoption process and implement the right strategies to increase the adoption rate. Only then will you see real results and you will be able to make your business successful.