We, humans, fancy ourselves to be the most rational beings. We are not as rational as we think we are. Our brain, though more capable than the smartest computer on earth, has several barriers that stop us from thinking logically. Many biases due to past experiences, feelings and emotions direct our decisions which may not be perfect.
Cognitive biases happen because of six reasons:
- Memory: when we misremember events
- Social: going with group thinking
- Learning: relying on early learning
- Belief: holding on to what you think is true
- Money: your outlook on money
- Politics: using political affiliations to make decisions
These erroneous judgments are called cognitive biases, that is, the error that we make when we are processing information and making a decision is called a cognitive bias. Typically, more than one of the above factors affects every cognitive bias that we form.
Cognitive Biases and Marketing
How do cognitive biases affect marketing? Marketers make hundreds of decisions per day and it is, therefore, vital that they understand the different cognitive biases well. This will help them as they meet hundreds of potential customers on a single day and are trying to get as many conversions as possible.
Different Cognitive Biases a Digital Marketer Should Know
1. Decoy Effect
Also called the asymmetric dominance effect, this happens when we are presented with two options and we have difficulty choosing between the two, However, the addition of a third option that is less attractive (the decoy) influences our perception of the first two.
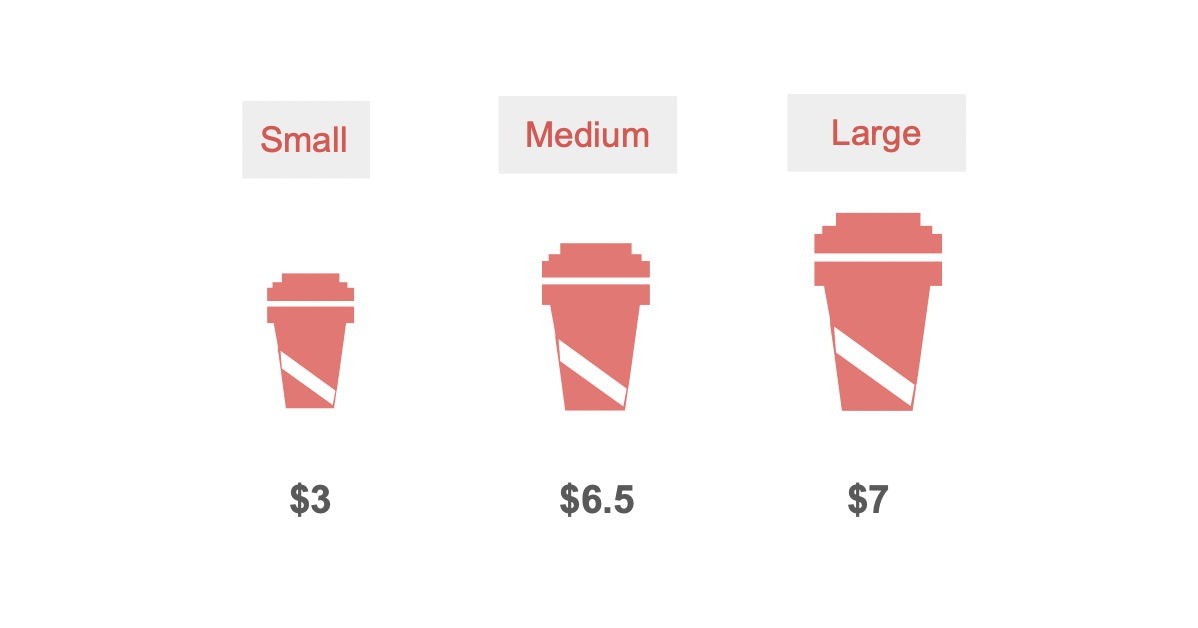
Here is an example of decoy effect when you are buying a beverage. There are three options, small, medium and large. You end up buying the large one because it is a much better deal than the other two. You spend more than what you need because of the decoy effect. Here, the choice is based on what feels like the best rather than what suits us the best. Digital marketers can take advantage of the decoy effect to sell higher value products, which will eventually increase AOV and overall revenue.
2. IKEA Effect

(image source: Sketchplantations)
IKEA effect cognitive bias occurs when we tend to place more value on products that we create rather than the ones that come assembled. Named after the Swedish manufacturer retailer, our own efforts make us place more value (overvalue) on the fruits of the job done when we complete the task. Digital marketers can include DIY elements in their products. Providing customization options is the way out for digital marketers.
3. Authority Bias
We sometimes are ready to implement whatever an authority figure says. This is because of authority bias which creates a tendency in us to be mindlessly influenced by an authorized person’s opinion because we think they have more knowledge and skills than we actually do. Industry leaders’ endorsements can be used strategically by digital marketers for products/services.
4. Zero Risk Bias
We are wired to love certainty, even when it is most counterproductive. Think of a situation when you are provided with two alternatives: you can take a risky route to win a jackpot, or you can take a longer but safer route to earn a decent sum of money. You will eliminate the risk by choosing the longer route.

Above is an example from Zoho Social (social media management tool), which highlights no credit card required and the users can switch plans anytime, plus it gives access to all features so that customers can experience and see the value of it. So when you eliminate the risk totally, there is simply no barrier to try the product. In digital marketing, presenting a product or a service as risk-free can enhance its effectiveness. A consumer is more likely to buy a low-risk product/service. It could be as simple as convincing your customer to try the product at zero risk.
5. Scarcity Effect
This is a technique that marketers use frequently to make customers make their purchases that are low on supply and high on demand. If you are a marketer, you can shorten the time frame and ask the customers to make a promotional purchase before the end date. After all, everyone loves to possess something that others do not have.

You will observe these on most of the e-commerce platforms, it’s a good practice to increase conversion rates
6. Reciprocity Effect
The principle of reciprocity describes our feeling of wanting to give something in return for something that we receive. Digital marketers can take advantage of the reciprocity effect by offering a free but valuable resource in lieu of a potential customer’s email id. The potential customer is most likely ready to part with their email-id when such an offer is made.
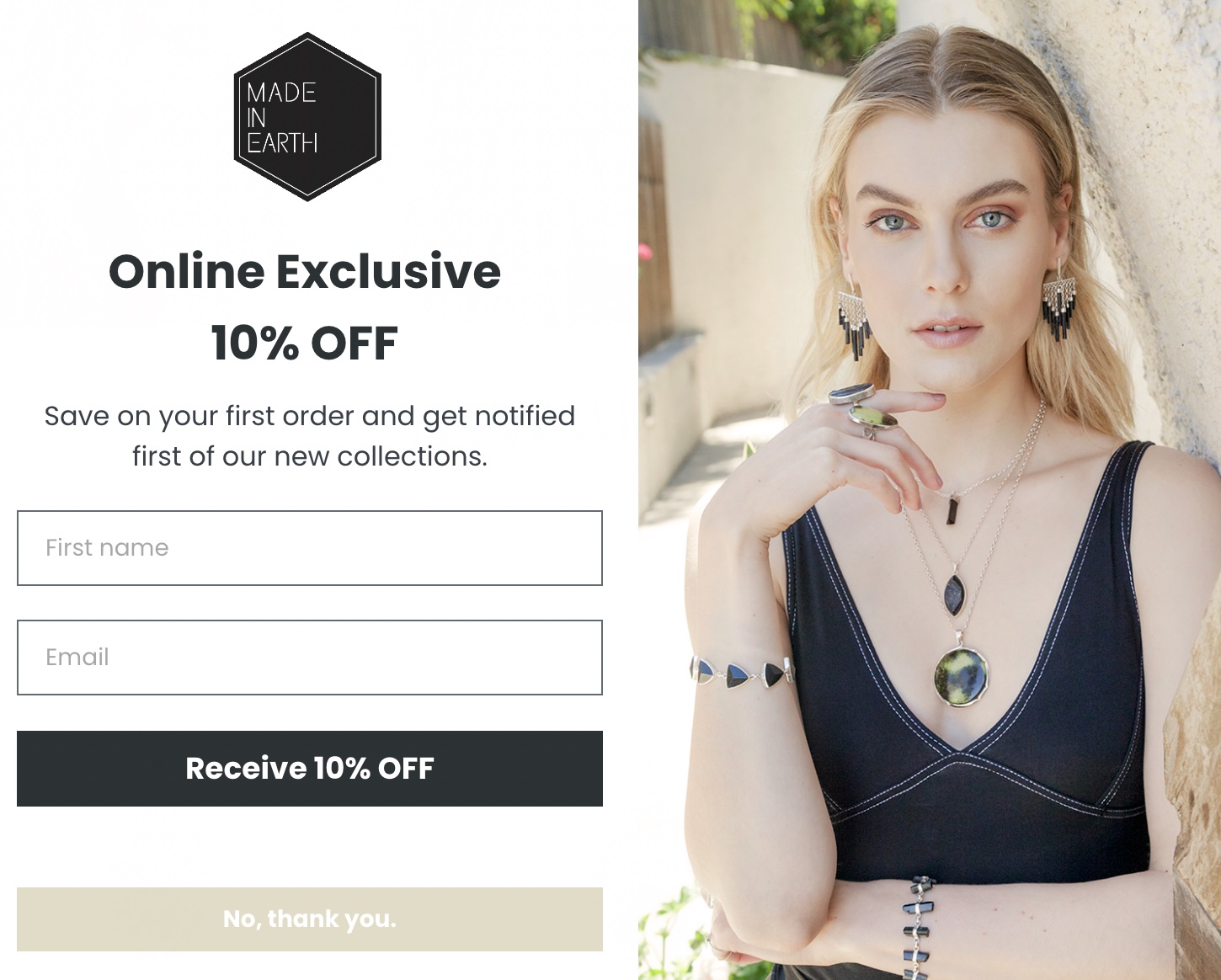
Here is an example of Made In Earth, where in the customers get 10% discount and also notified first on new collections if they share their email address
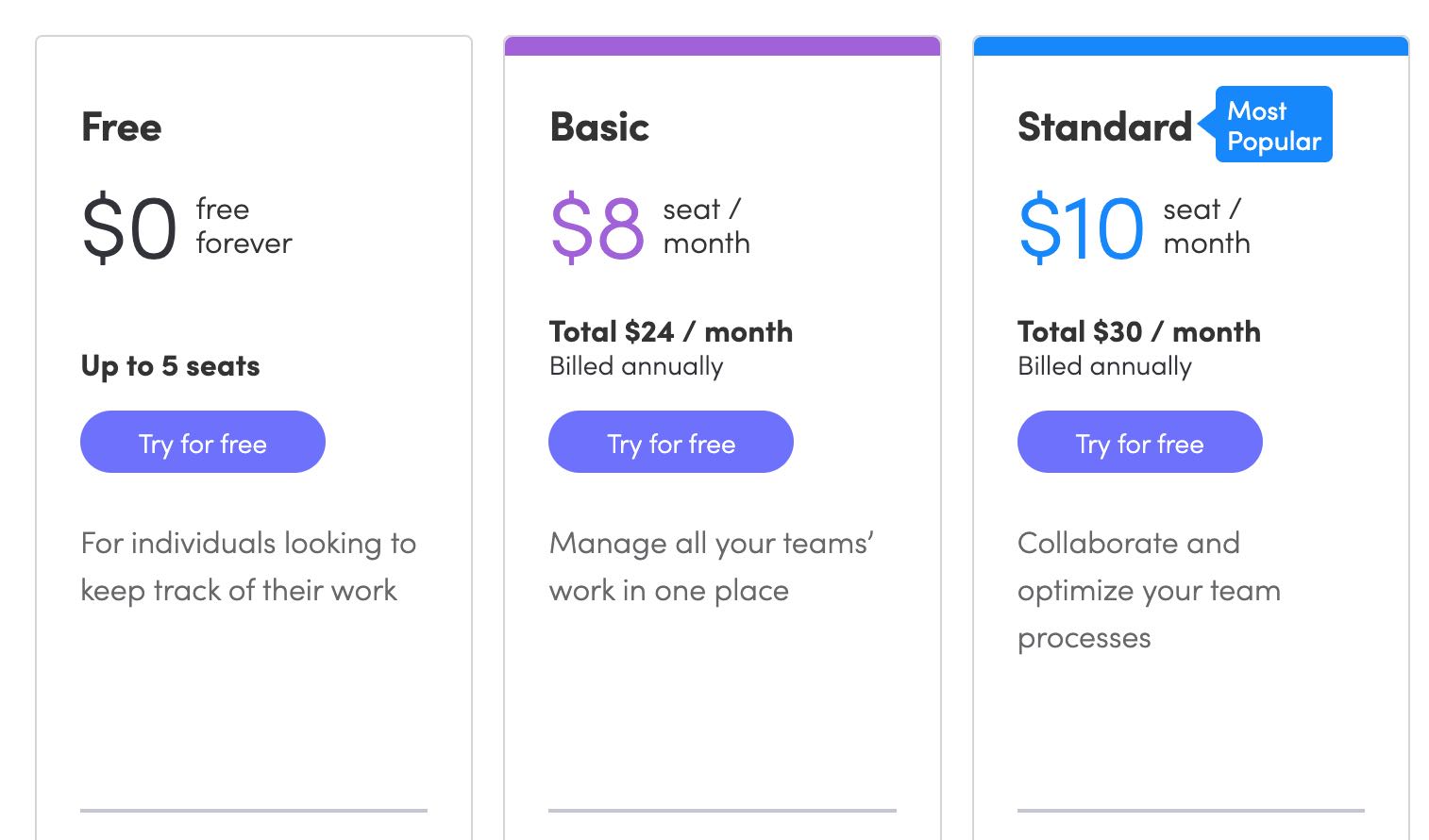
7. Foot-in-the-door Technique
Often used in marketing and sales, this technique is based on compliance and consistency. If a person complies with a small request, in the beginning, there are greater chances of the person agreeing to a larger request later on.
Here is an example by Monday (project management tool), where 5 users within a team can try the product for free, post that the company charges $8 per user per month, which means Monday got the users onboard free, and now they encourage to go for paid versions with more options
8. Framing Effect
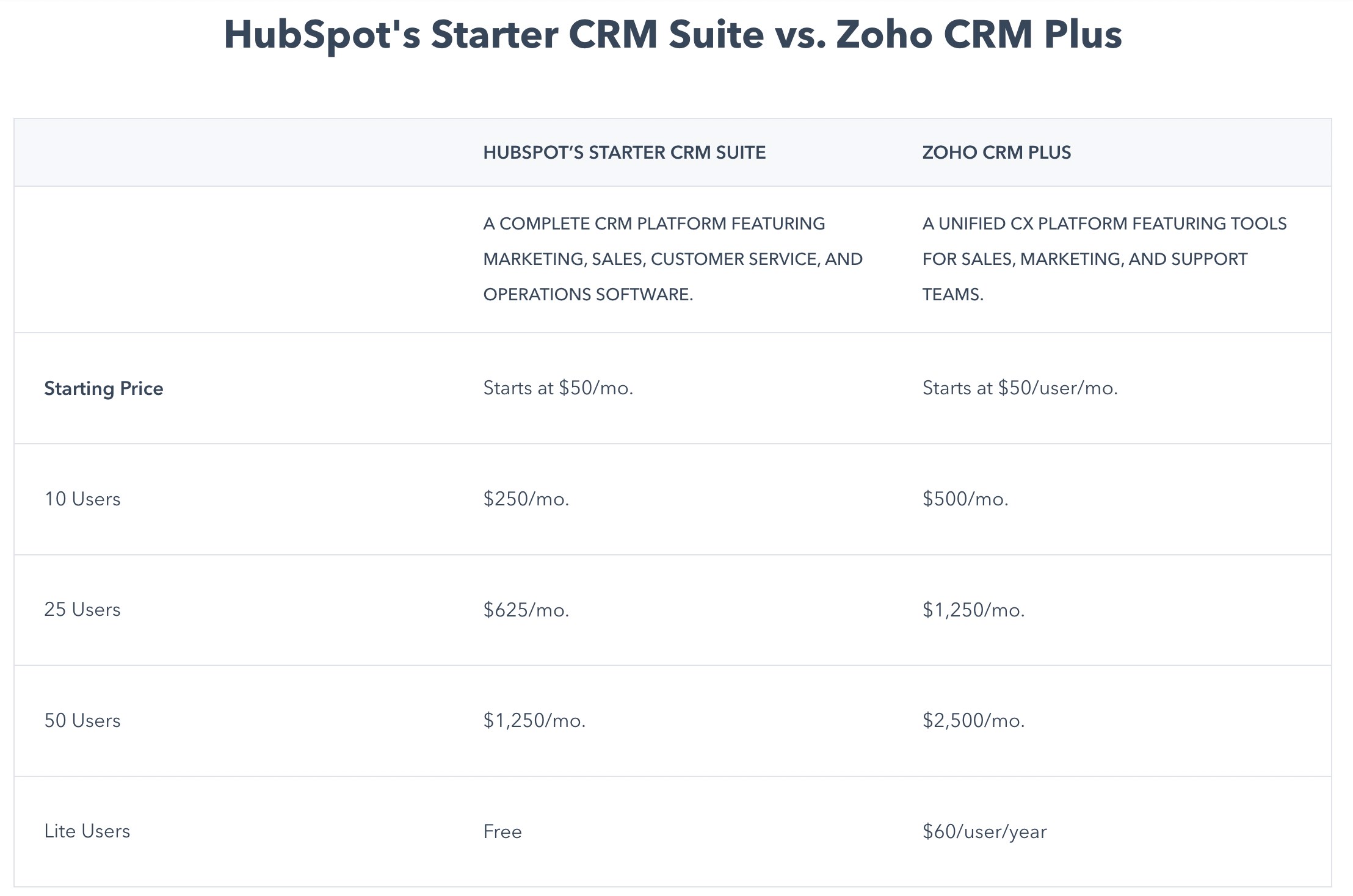
The framing effect is used by marketers to influence customers. Different people react to the same information if presented differently, in different ways. While a specific company may promote its product as having a 90% success rate, its competitor may come out with a counter-frame saying that the former company’s product may have a failure rate of one in ten times. It is like perceiving whether a glass is half full or the same glass is half empty.
Below is an example of how Hubspot compares it’s CRM with Zoho CRM plus, which gives clear indication of how cost effective the tool is compared to Zoho
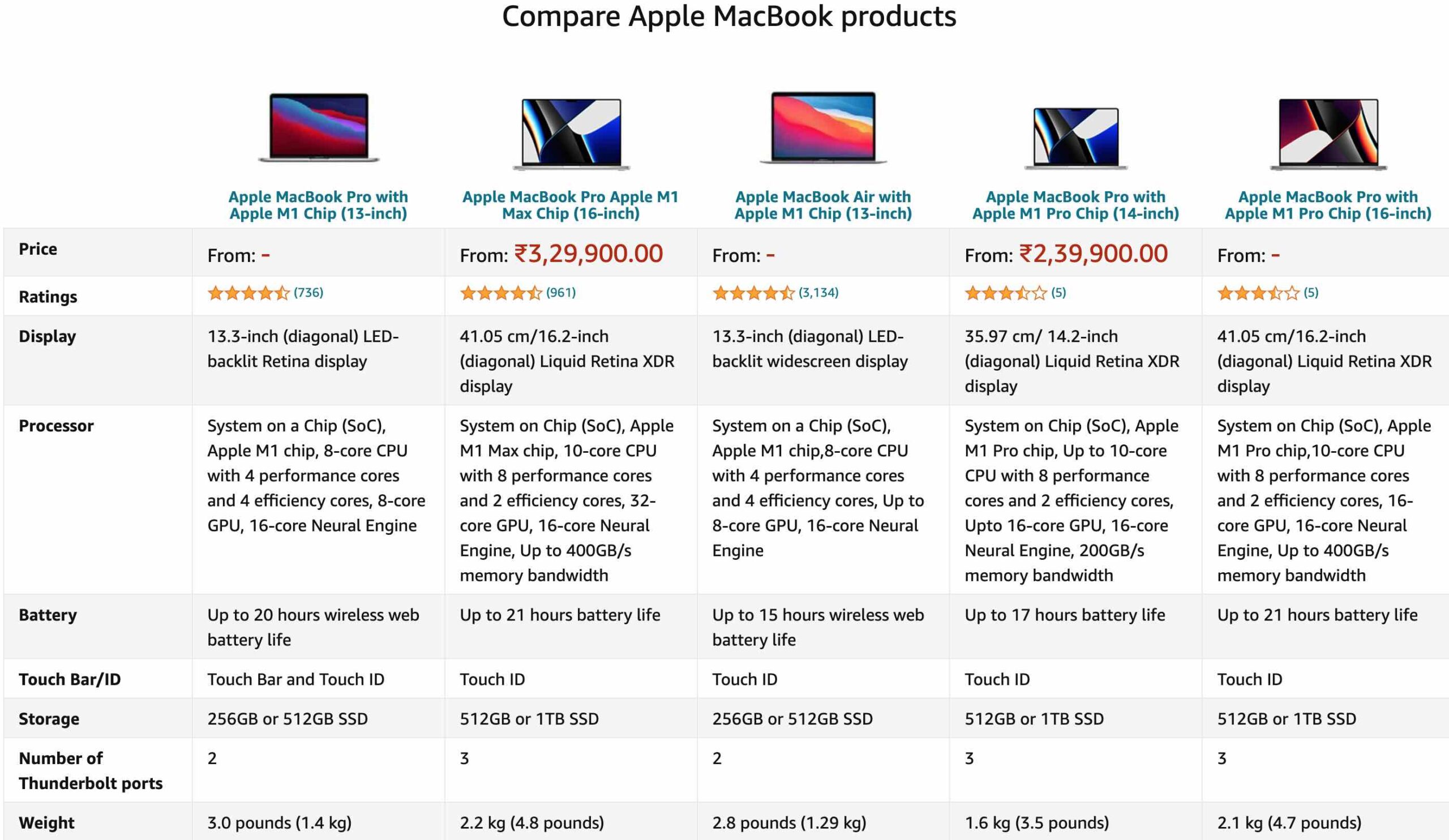
9. Analysis Paralysis
Analysis Paralysis is about information overload, which delays the decision making process.
Here is an example from Amazon where you see multiple products options with lot of options, customers might be overloaded with information and delay their decision. It is recommended to have only 3 options so that customers can make quick decisions.
10. Choice Supportive Bias
If you opt for something, you tend to feel positive about it even if there are flaws in the choice. In digital marketing, you can take advantage of this aspect by creating a desire in the mind of the consumer. They will make the purchase and later justify this purchase even if the choice was illogical.
Amazon pushes recommendations based on your shopping history, which motivates you to go for similar products which you have bought in the past, though the products might not have good features.

11. Fluency Heuristic
This principle suggests that users tend to pick up that option they can process the fastest which they think is the best choice. If an idea is communicated to the buyer skilfully, they are likely to bite the bait.
Here is an example of Hubspot, it communicates the product message clearly and also mentions free for everyone. So as a customer I would be motivated to go for the CRM after reading the key communication.

As a digital marketer, keep your communication concise and precise, so that customer understand the product and the value it brings to them
12. Variable Rewards
People are tuned to enjoy unexpected rewards. Rewards motivate customers to go for the product. It’s a great way to get the customer hooked during the acquisition journey
Here is an example of CRED, it has different jackpot reward options for different products.
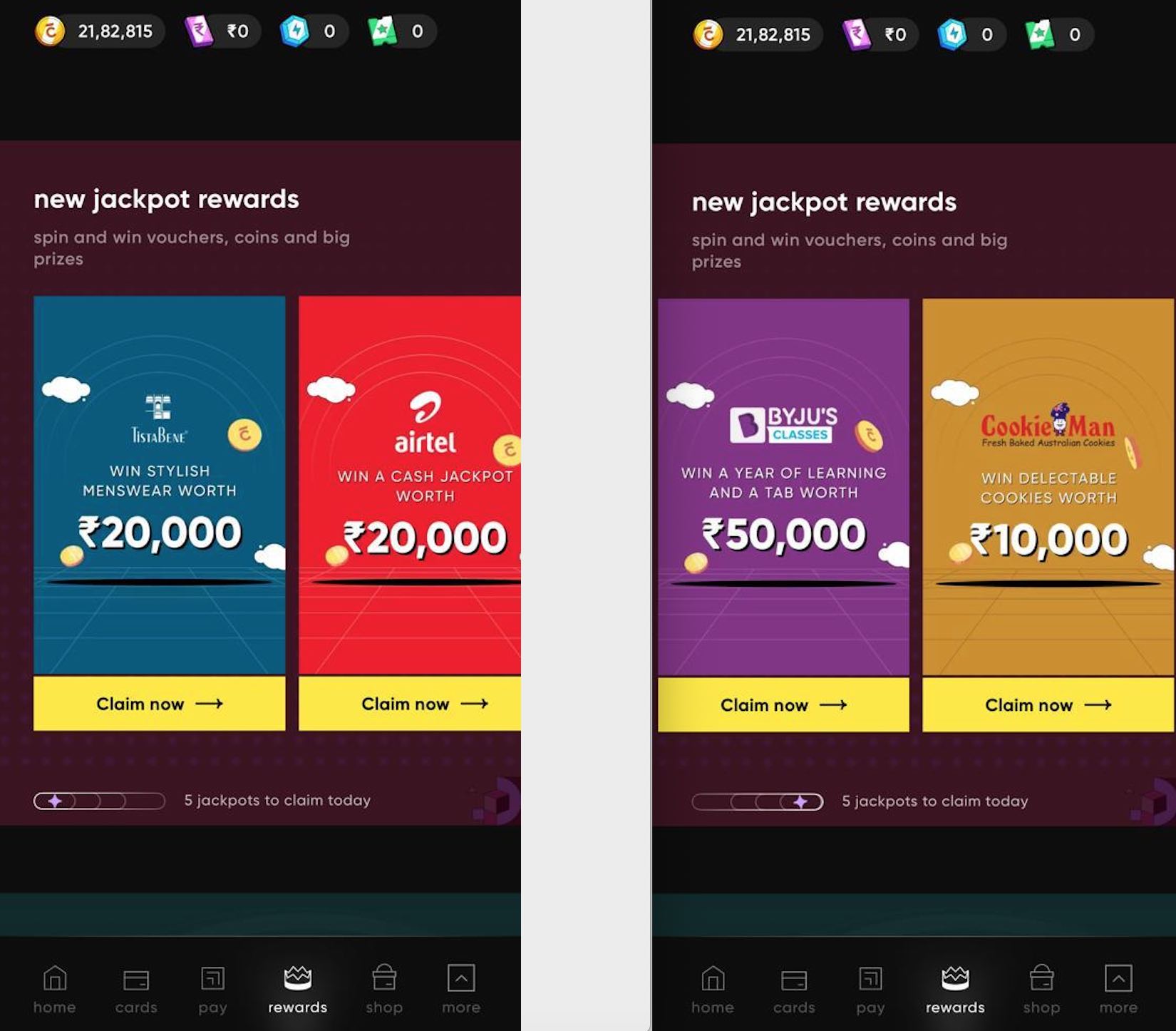
Further CRED has pay rewards, when a customer pays, they are eligible for rewards
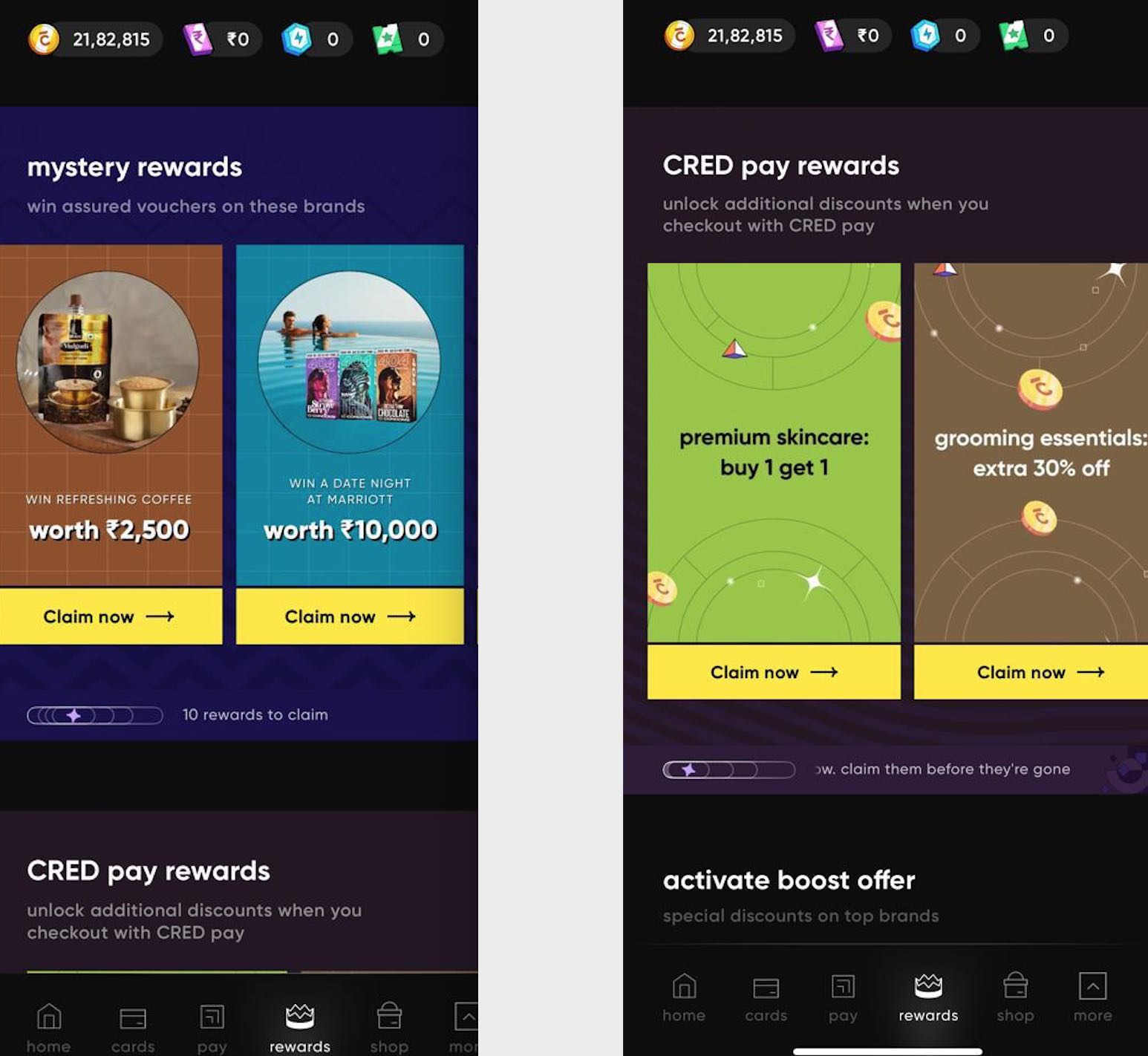
Several commerce brands use variable rewards strategy to encourage customers to make a purchase. Digital Marketers can leverage this strategy to improve overall sales on the store.
13. Restraint Bias
Individuals generally try to overestimate the capacity of their ability to resist temptations. The more the brand offers, it’s difficult to resist.
Amazon prime video does it in a great way, if you are watching an episode, due to the autoplay option, you might end up watching an entire episode.

Here is another example by Udemy, when the customer is trying to by a course, similar courses are pushed at the cart level, so the customer might end up by another course, which will ultimately increase the cart value.
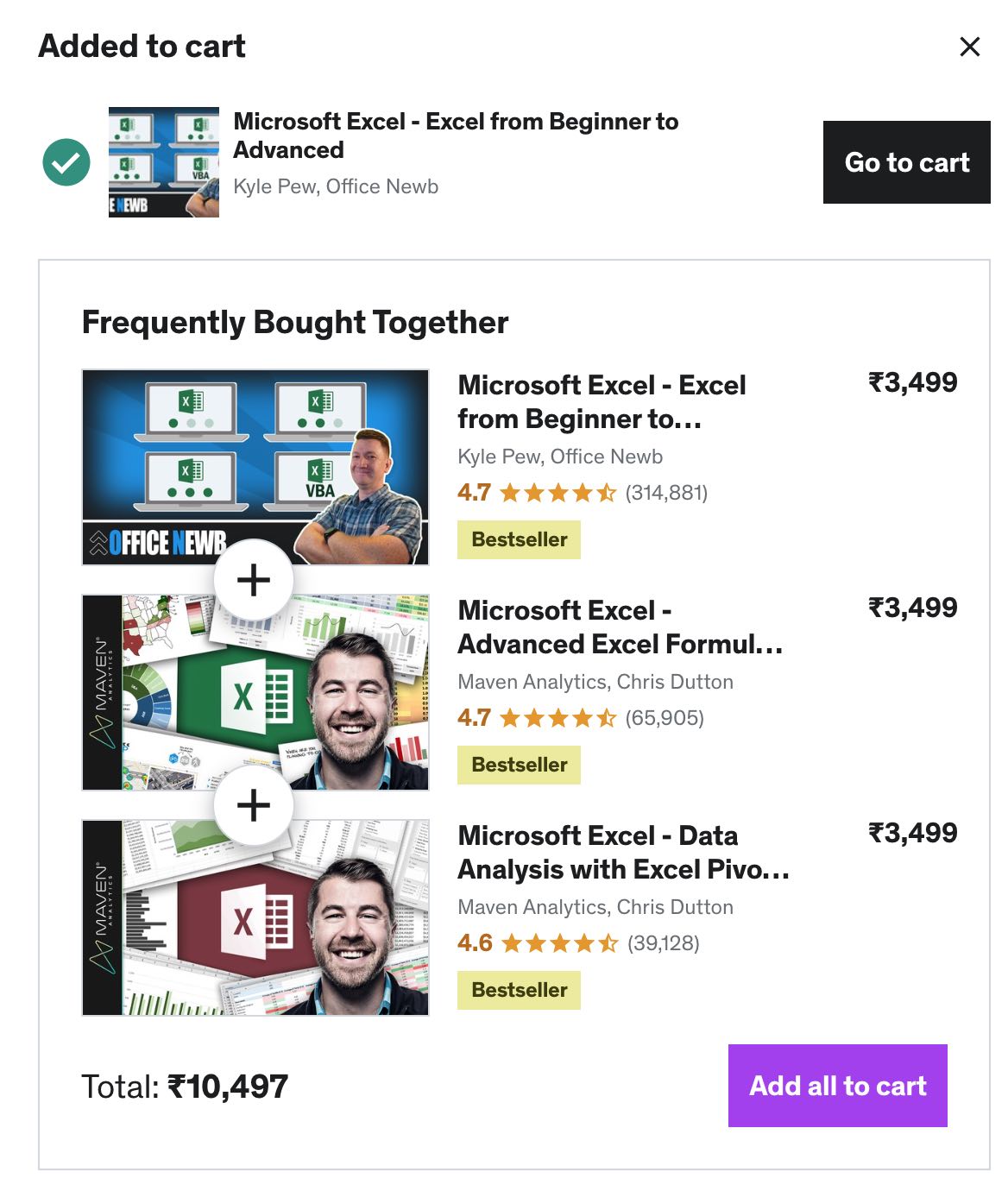
Digital marketers need to finds ways how they can keep the audience hooked on the platform, or encourage them to buy more.
14. Distinction Bias
This is the tendency of individuals to view two options as being more dissimilar when analysing them simultaneously than when separately.
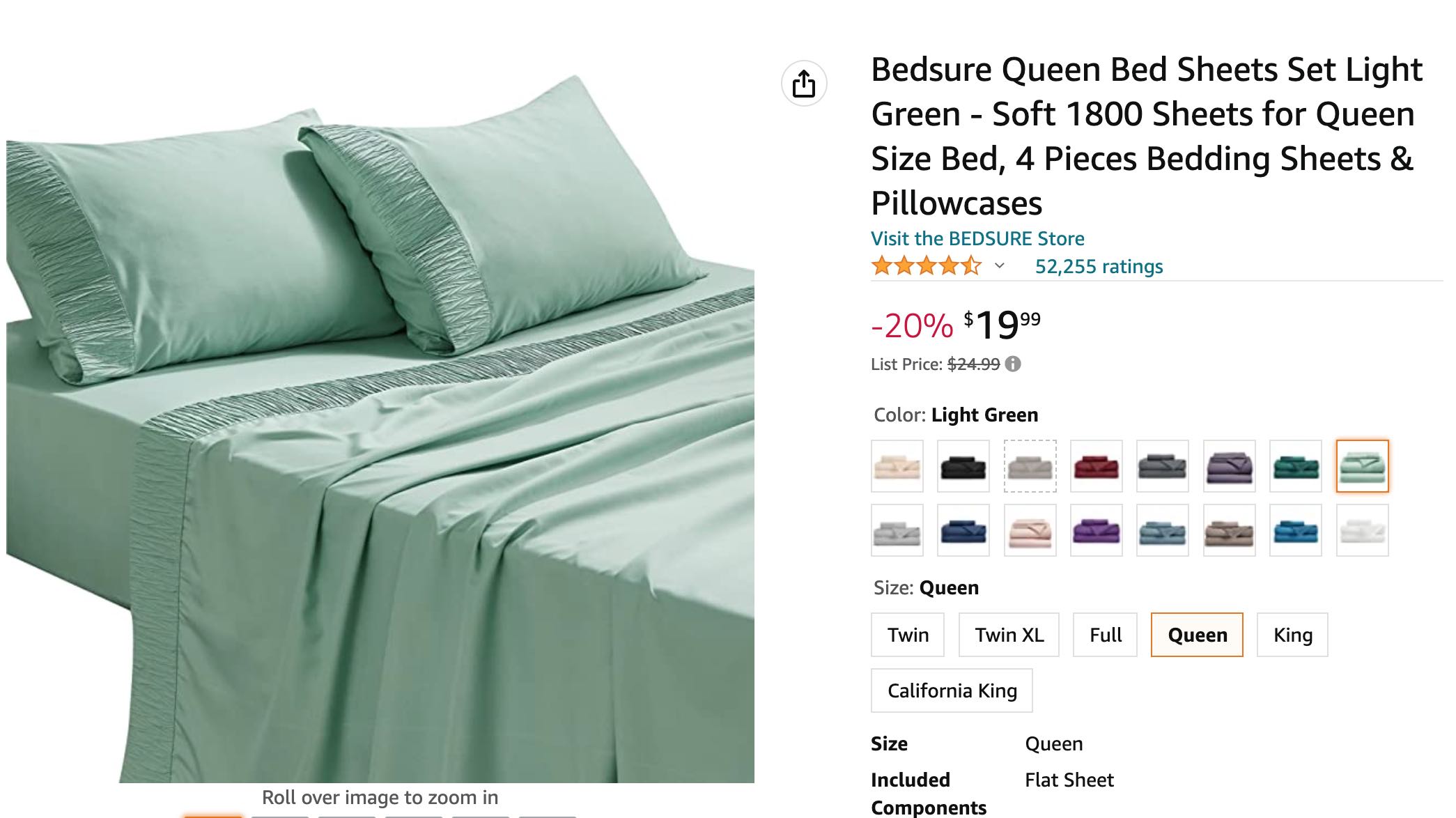
Amazon does well, in the above example you can see, how Amazon offers different colours to choose from, plus it allows to select the size of the bed sheet, and based on the all the selections the price also changes. This gives opportunity to customers to choose from multiple options.
As Digital Marketers you need to showcase value through comparison, so that customers are influenced to go for the best product based on their needs.
15. Weber-Fencher Law
Also called the sensory perception law, any sensory response to stimuli is not proportional to the strength of the stimuli. Detection happens when the difference in strength is large. In digital marketing, this means small price variations do not really matter to the buyer. The perception is strong when the size of the change is large.
16. Serial Position Effect
It is always easy for anyone to remember the first or last items on a list. Hotjar (behavioural analytics tool) does it well while defining their pricing.
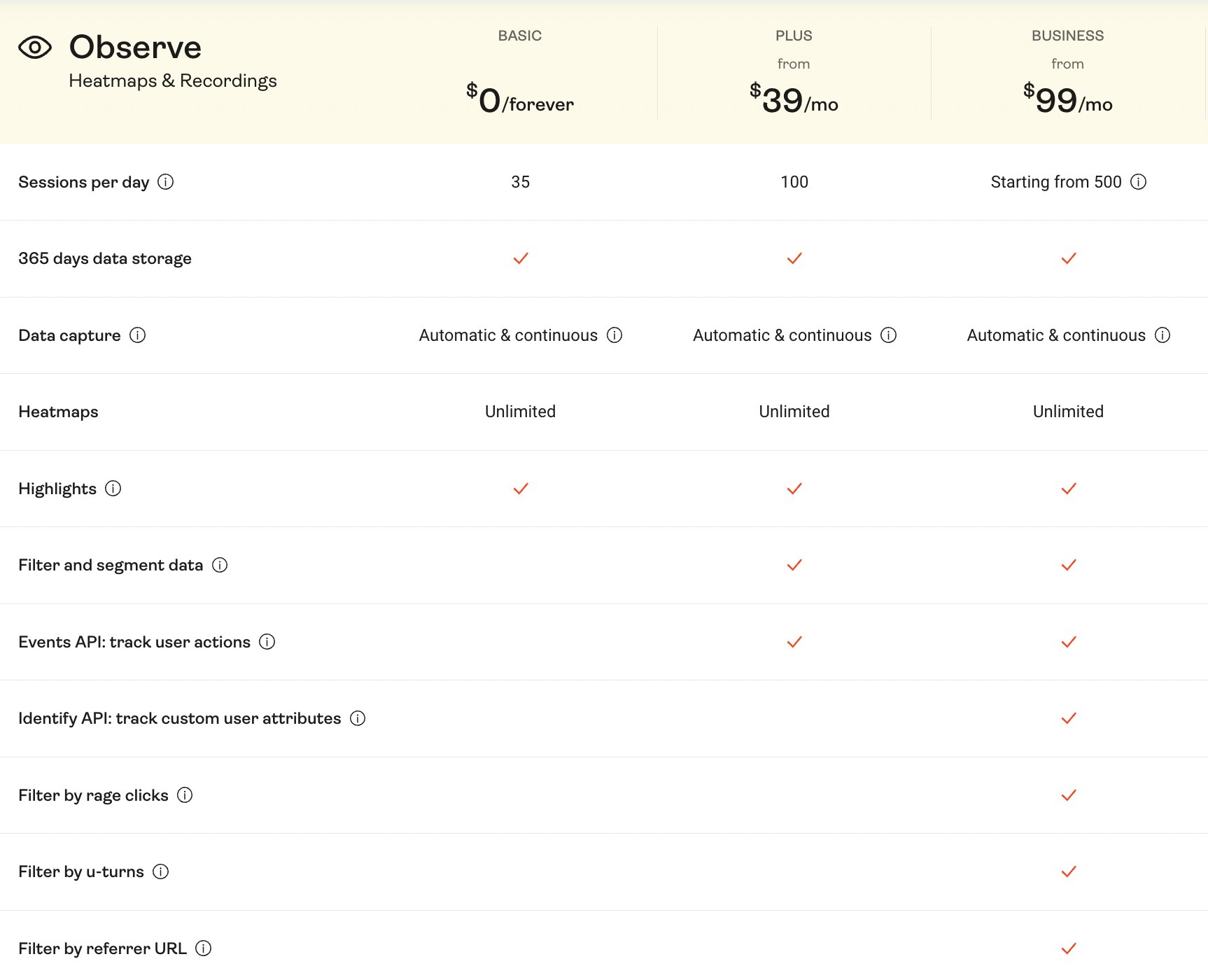
Digital Marketers can use serial position effect to differentiate pricing for their products and place the one’s which they want to get maximum attention for.
17. Zeigarnik Effect
Individuals remember incomplete tasks better than completed ones. Here is an example from Google My Business which says your profile is 85% complete, improve your local search ranking and help your customers with a complete profile.
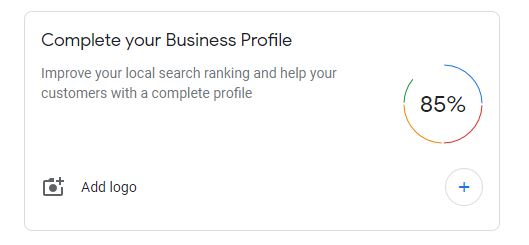
Digital Marketers can use progress bars or completion percentage, with a message which motivates to complete the task. If the customer is midway, marketers can use Zeigarnik effect to complete the purchase act.
18. Anchoring Effect
This is a cognitive bias that indicates the human tendency to rely too much on the first piece of information (the anchor) they are exposed to. Any other information that is received afterwards is viewed relative to the first one.
For example if you see a t-shirt for $1000 and then see another one for $300, you would feel, the second one is cheap, but if you see only the $300 one, you might not consider it as cheap.
When digital marketers try to sell a product, it is a good idea to first set the price slightly higher than what they would expect to get. Any other offer that the buyer encounters will be relative to this anchor price. The buyer may settle for a slightly more expensive package (but unnecessary) than a cheap one thinking they are on to a good deal.
19. Bandwagon Effect
The bandwagon effect refers to a tendency of people to adopt a specific style or behaviour because many others are doing it.
Here is an example by Monday, which highlights 152k customers trust it, and also few names of the companies. After looking at this, it will definitely influence your decision.

The perceived popularity of a brand quickly instigates the bandwagon effect. If a digital marketer creates the effect that their brand is a popular one that most people go for, many others are likely to signup for the brand or purchase the product
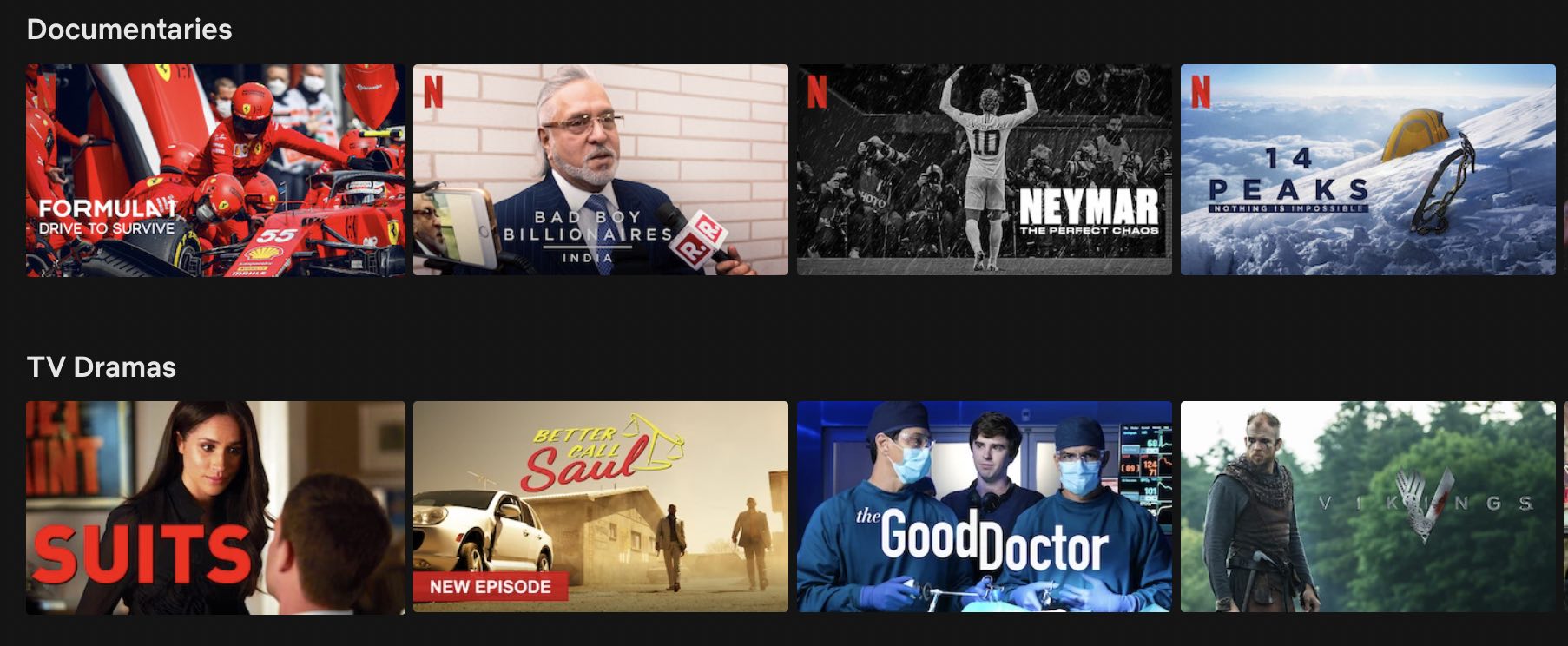
20. Barnum-Former Effect
The Barnum Effect is also called by the name Forer Effect. It refers to the phenomenon when individuals believe that personality descriptions apply exclusively to them. In actuality, these descriptions may have been defined for everyone.
Barnum Effect is used by many modern digital businesses. Personalising their ware, such as personalized music/movie lists gives the user a certain amount of satisfaction because they believe the options are personalized exclusively for them and then tend to engage with it. Netflix does it well, based on the users viewing history, it personalises the feed, so that the user is interested further in exploring more options to watch.